Chap.7 Synthesis of molecules for the membranes of the cell
7.1 Collision between H+ of the solar wind and CO2 of atmosphere
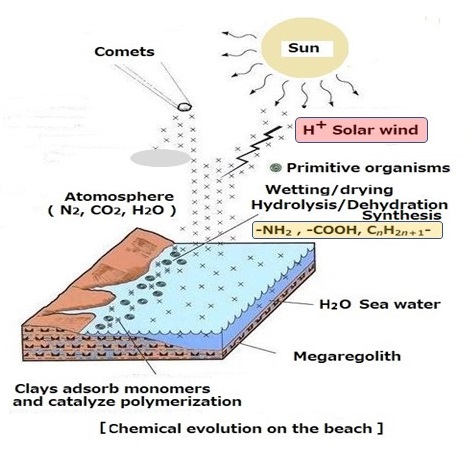
Fig.13 Organic molecules produced by the collision of atmospheric CO2 with the H+ of the solar wind
S. L. Miller, who experimented with the first process of life development using methane, hydrogen, and ammonia as the atmospheric composition of the primitive Earth. Subsequent studies have led to the thought that the atmosphere at the period of the birth of the first life was mainly composed of oxidizing gases such as CO2 and NOx, However, there filled with H+ in the upper sky, and those ions make chemical reactions with CO2 of the Earth's atmosphere.
7.2 Membrane of hydrocarbon organized on the water surface
High-speed H+ and CO2 of primordial atmosphere collides to produce water and hydrocarbons. The hydrocarbon molecules with a small number of carbons evaporate on the surface and remain in the upper sky. However, hydrocarbon molecules with many number of carbon atoms exist on the Earth's surface as liquids. Those hidrocarbon molecules are higher boling point mohe then surface temperature on the graund.. Hydrocarbons, in which two carbon atoms are bonded and linked together, are formed by hydrogen atoms to form molecules on a straight line.As shown in Table 1, hexadecane and octadecane existed in a liquid state in the primitive Earth environment, were hydrophobic, insoluble in water, and spread on the surface of water because their specific gravity was less than 1. Linear hydrocarbon molecules with 16 or 18 carbon atoms were suspended on the surface of the water due to hydrophobic bonds. The main components that make up the cell membrane of living organisms are linear hydrocarbons with 16 or 18 carbon atoms.
Table 2 Physical properties of linear hydrocarbon molecules with 14, 16, 18, and 20 carbon atoms
| Formula | Melting [℃] | Boiling [℃] | Gravity [20℃] | |
| Tetradecane | C14H30 | 4 to 6 | 253~257 | 0.76 |
| Hexadecane | C16H34 | 18 | 287 | 0.773~0.776 |
| Octadecane | C18H38 | 28~30 | 317 | 0.777 |
| Icosane | C20H42 | 36~38 | 343.1 | 0.7886 |
7.3 Systematic thermal motion of H2O molecules in liquid water
Water molecules in liquid state are three-dimensionally connected by hydrogen bonds, and the configuration of the most contracted molecules is α-quartz which is a crystal-shaped of a spirl structure. In the spiral structure, when the tetrahedron is rotated alternately with the electrical axis as the axis of rotation, the tetrahedron projected on the X-Y plane becomes trapezoidal as shown in Fig. 14.
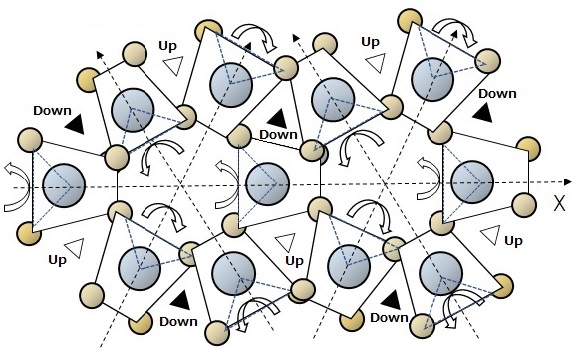
Fig.14 Systematic thermal motion of the spiral-type arrangement of molecules H2O
to index -7.1-